REMINDER
Advanced SQL Field Types
-
@wassim Maybe I'm just over-complicating things, but I'm getting JSON like this:
{ "Table": [{ "Published": 1, "Person_relation": ["1","2","3"] }, { "Published": 1, "Person_relation": ["1"] }, { "Published": 1, "Person_relation": ["1"] }] }So I wanted the ID to be replaced with the name value from that table relation column in one query, so it would return this instead.
{ "Table": [{ "Published": 1, "Person_relation": ["Mike", "Steven", "August"] }, { "Published": 1, "Person_relation": ["Mike"] }, { "Published": 1, "Person_relation": ["Mike"] }] }I could of course do this in code, but I wanted to make it with SQL only if possible.
-
Hey Thomas, just use Linked Fields by Value instead of By Reference and that's exactly what you will get

-
@Joseph-Benguira That's what I did at first, but that breaks the link entirely when the data changes in the source table.
-
Ah I see, you can handle that in business logic when you rename through your UI a data to do the corresponding UPDATE in SQL ... or handle this at runtime with a dictionnary ... We can't return directly the merged structure because it would be a major hit to perf.
Database do that 100x faster with JOIN in SQL.
That way you can do a SQL query with JOIN that will return exactly that in JSON (and still storing by reference)It's always a tradeoff and you have to choose the best solution for your use case
You can do basic things easily, you can also do advanced things with SQL or code
but you can't do Advanced things without Code and without SQL -
Yeah, I'm trying with the reference ID and a query to use GROUP_CONCAT and join and group to do it and use an index to keep it fast, should work well enough..
I've only every used NoSQL my whole life, so MySQL is a bit of a challenge

About time I learned it though
-
I'm failing to produce what I need, the field doesn't seem to be a foreign key with a reference as it claims to be, but just a text field with the array ID's.
I'm guessing you have custom logic behind that, but I fail to know how to use the ID's other than as only static values.
-
What you can do in the cloud function is to make 2 queries, one to get the main data, and another one to get the references from your ref table, then loop on the main results and enrich them based on what you have in the ref table. So this solution is few lines of node.js
There is another way we also use quite often, the idea is to return the data with the refs in an array and in the same api call also return the dictionnaries
E.g: in your node.js function
var result = { rows: yourRowsHere, dic: rowsFromAnotherQueryToYourRefTable }; callback(null, result);Then in the frontend code use the dictionnary when interpreting the rows.
-
Ideas:
-
At first my idea was to use what you suggest, use node to make calls of each referenced table row, but I thought using joins would be faster. Plus, the automatic database GUI forms could not be used when using several separate tables.
-
The dictionaries idea is interesting, we could gather all the ref unique ID's and combine that into an array of ID's that is needed for the request and fetch that only once. This should be faster than a join because we'd not be fetching the rows multiple times for every item.
-
Seems like it's easy to choose a design that would be limiting though, a proper many-to-many relation would enable more features while persisting performance. But it would mean we'd have to make custom input forms/functions and write raw db queries.
I'll compile this into a how-to when I've tested it more.
(I managed to get a join query working on the arrays btw)
-
-
@Joseph-Benguira By the way, is there any way I can test the query performance?
-
You can run the in "New Query", this is returning the execution time in miliseconds of your query
Another great thing you can do to improve query speed is to add indexes on your tables on the fields you are using in WHERE or JOIN conditions. You can get a 100x improvement with indexes
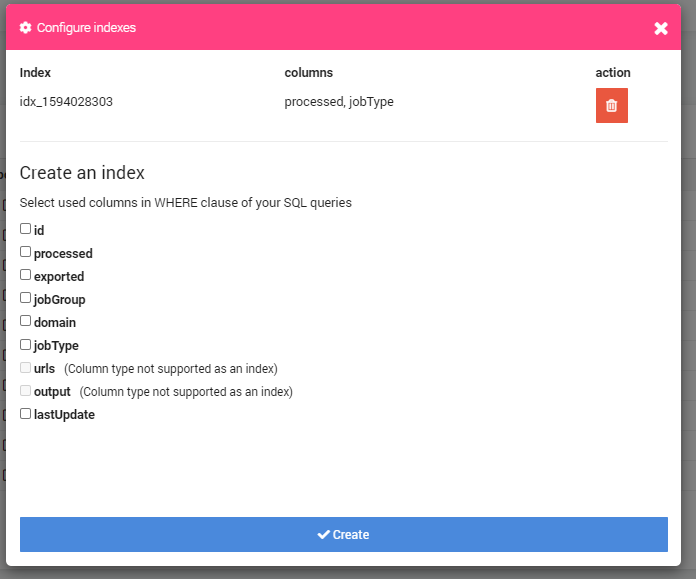
It's accessible from the EDIT button when you are inside a table